Irregular Periods
Irregular menstrual cycles may indicate the presence of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), a condition that can contribute to infertility.
Female infertility refers to the inability of a woman to conceive or carry a pregnancy to full term despite having regular, unprotected sexual intercourse for an extended period, typically one year for women under 35 and six months for women over 35. Infertility can result from various factors, including:

Irregular menstrual cycles may indicate the presence of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), a condition that can contribute to infertility.

Many women experience cramps for a day or two during their periods, which is typically manageable. Such symptoms could indicate the presence of endometriosis, a significant marker for infertility.

Hormonal fluctuations can often be subtle and nonspecific. Some hormonal issues can be diagnosed through medical testing conducted by a doctor.
Some women feel pain during sexual intercourse. However, this discomfort may be linked to hormonal imbalances, endometriosis, or other conditions that could contribute to female infertility.
Irregular vaginal discharge serves as a subtle yet significant marker of potential female infertility. Alterations in its texture, hue, or odor could signify underlying issues warranting attention.
The initial stage in fertility treatment involves identifying the factors contributing to infertility. Various fertility tests may be employed to confirm an infertility diagnosis in women. When conducting infertility tests, physicians typically begin with a physical examination of the patient and inquire about her medical history and lifestyle. Additionally, one or more of the following tests may be recommended:
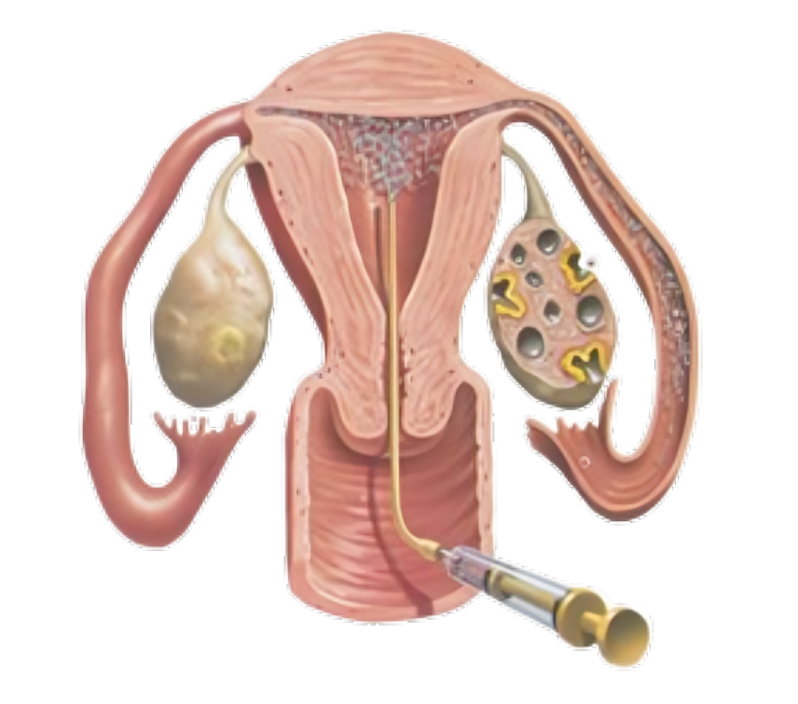
It involves injecting a liquid dye into the uterus via the vagina. X-ray images are then taken to track the movement of the dye through the fallopian tubes. If there is an obstruction, the dye will be unable to pass through, indicating a potential issue.
This test is performed to assess the ovarian reserve, indicating the quantity of eggs available for ovulation. Typically conducted at the onset of the menstrual cycle, it helps evaluate reproductive potential.
The pelvic ultrasound test is employed to identify potential uterine or ovarian disorders. It is particularly useful for detecting uterine conditions that may not be visible on a standard ultrasound.
This step involves assessing levels of ovulatory hormones as well as pituitary hormones that play a crucial role in reproductive processes.
After diagnosing infertility and identifying its cause, your healthcare provider will propose potential treatment options tailored to your specific situation. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause of infertility. Some of these treatment options include:
Laparoscopy enables the identification of fertility issues that might otherwise escape detection such as mild endometriosis...Read More
During a hysteroscopy, the hysteroscope is gently guided through the cervix into the uterus. The hysteroscope...Read More
During IVF, mature eggs are retrieved from a woman's ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory dish...Read More
In IUI treatment, sperm is directly inserted into a woman's uterus during ovulation. The goal of IUI is to ...Read More
It involves individuals or couples utilizing a third party, such as a surrogate mother or a sperm or egg donor... Read More
Women are typically born with around 2 million eggs in their ovaries. Prior to puberty, approximately 11,000 eggs perish each month. Consequently, by the time a girl reaches her teenage years, she's left with roughly 300,000 to 400,000 eggs. As she ages, about 1000 eggs are utilized each month, independent of factors such as birth control, pregnancy, hormone production, health, lifestyle, or nutritional supplements. Ultimately, menopause occurs when a woman exhausts her egg supply.
Common causes of female infertility include hormonal imbalances, ovulation disorders, blocked fallopian tubes, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), uterine abnormalities, and age-related factors.
Yes, lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, poor diet, stress, and exposure to environmental toxins can impact fertility in women.
Female infertility is diagnosed through a series of medical tests, including hormone level testing, ovarian reserve testing, imaging studies (ultrasound, hysterosalpingography), and laparoscopy to evaluate the pelvic organs.
Signs indicating male infertility encompass challenges in conceiving following over a year of unprotected intercourse, anomalous results from semen analysis, reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, and hormonal imbalances, among others.While not all causes of female infertility can be prevented, adopting a healthy lifestyle, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and seeking timely medical care for reproductive health issues can help reduce the risk of infertility.
Female infertility affects approximately 10-15% of couples worldwide. It is a widespread issue that can significantly impact individuals and couples seeking to conceive.