Preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A), formerly known as preimplantation genetic screening (PGS), is a procedure used during in vitro fertilization (IVF) to screen embryos for chromosomal abnormalities before they are transferred to the uterus.
Aneuploidy refers to an abnormal number of chromosomes, which can lead to genetic disorders or unsuccessful implantation. PGT-A helps identify embryos with the correct number of chromosomes, increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy and reducing the likelihood of miscarriage.
Preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A), formerly known as preimplantation genetic screening (PGS), is a procedure used during in vitro fertilization (IVF) to screen embryos for chromosomal abnormalities before they are transferred to the uterus.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy (PGT-A) is primarily conducted by fertility clinics and laboratories specializing in assisted reproductive technology.
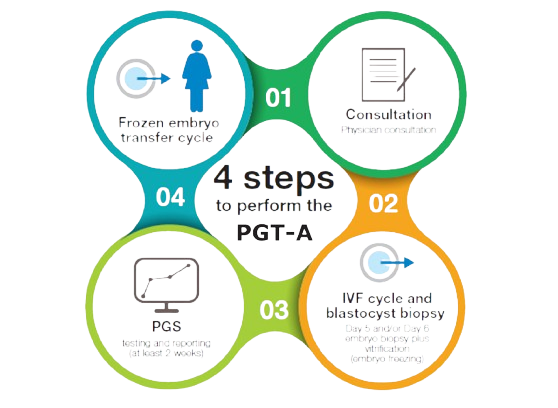
"PGT-A aims to improve IVF success rates by selecting embryos with the correct number of chromosomes, known as euploid embryos, for transfer.PGT-A aims to improve IVF success rates by selecting embryos with the correct number of chromosomes, known as euploid embryos, for transfer.PGT-A aims to improve IVF success rates by selecting embryos with the correct number of chromosomes, known as euploid embryos, for transfer.PGT-A aims to improve IVF success rates by selecting embryos with the correct number of chromosomes, known as euploid embryos, for transfer.The PGT-A process begins with ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval, followed by IVF fertilization of retrieved eggs with sperm. Embryos are cultured in a laboratory until they reach the blastocyst stage, typically around day five or six after fertilization. At this stage, a few cells are removed from each embryo through a biopsy procedure, usually without harming embryo viability".
The purpose of PGT-A is to screen embryos for chromosomal abnormalities, specifically aneuploidy, which involves an abnormal number of chromosomes.
PGT-A involves removing a few cells from an embryo created through in vitro fertilization (IVF) and analyzing them to determine if there are any chromosomal abnormalities.
Individuals with advanced maternal age, a history of recurrent pregnancy loss, or known chromosomal abnormalities may benefit from PGT-A to improve the chances of a successful pregnancy.
PGT-A can detect various chromosomal abnormalities, including Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Turner syndrome (monosomy X), and other disorders resulting from abnormal chromosome numbers.